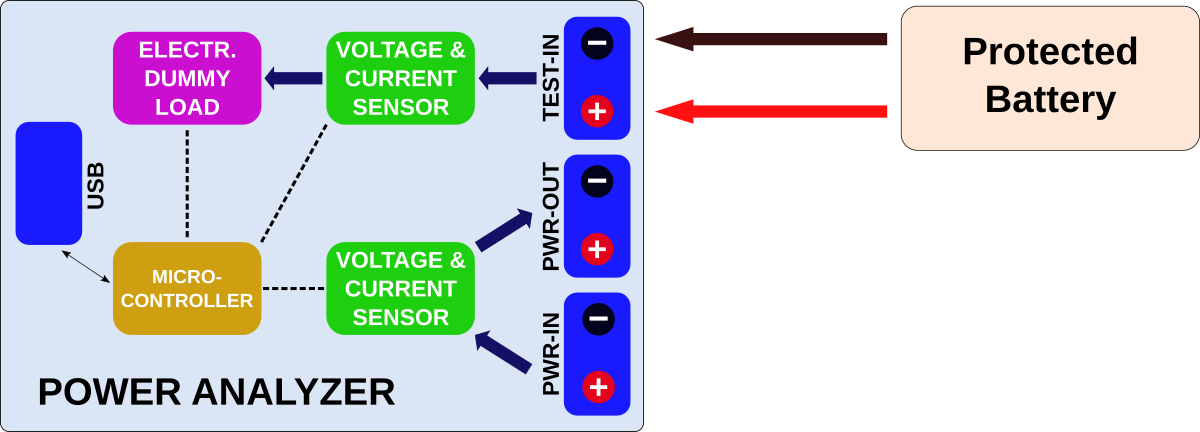
 # 2. Working Principle
The ATtiny814 controls the electronic dummy load with its internal digital to analog converter (DAC). All of its 5 internal reference voltages are being used in order to get the maximum accuracy and resolution of the DAC. The DAC is connected to an OpAmp which acts as a unity gain amplifier controlling the resistance of the MOSFET. Voltage and current are measured via a high side 8 mOhm shunt resistor connected to an INA219 with a resolution of 4mV/1mA. A second INA219 is connected to another 8 mOhm shunt resistor between the PWR-IN and PWR-OUT terminal. The Power Analyzer is connected via USB to a PC or a RaspberryPi. Commands to the Analyzer can be sent via a serial monitor or by the GUI-based Python skript. The Analyzer has different built-in automatic test algorithms. The collected data is sent back via the serial interface/USB to the PC/RaspberryPi. The ATtiny814 constantly measures power and temperature of the heatsink. It controls the fan and cuts off the load when the temperature gets too hot.

# 3. Test Algorithms
* Using a serial monitor: Test algorithms can be started by sending the corresponding command via a serial monitor. The collected data will be displayed in the serial monitor and can be exported to a spread sheet program for further analysis.
* Using the GUI-based python application: This is the easy way. Everything should be self-explanatory. All following example pictures are created by this application.
# **Load Test**

* Command: "l *maxloadcurrent[mA: 17..5000]* *minloadvoltage[mV: 0..26000]*"
* Example: "l 2500 4200"
* The Power Analyzer continuously increases the load from 17 mA up to *maxloadcurrent*. It stops automatically if the voltage drops below *minloadvoltage*. It continuously transmits the measured values via the serial interface in the format: current[mA] voltage[mV] power[mW] (seperated by the SEPERATOR string).

# **Voltage Regulation Test**

* Command: "g *maxloadcurrent[mA: 17..5000]*"
* Example: "g 3000"
* The Power Analyzer changes rapidly the load between 17 mA and *maxloadcurrent*. It continuously transmits the measured values via the serial interface in the format: time[ms] current[mA] voltage[mV] (seperated by the SEPERATOR string).

# **Efficiency Test**

* Command: "e *maxloadcurrent[mA: 17..5000]* *minloadvoltage[mV: 0..26000]*"
* Example: "e 4000 2500"
* The Power Analyzer continuously increases the load from 17 mA up to *maxloadcurrent*. It stops automatically if the voltage at TEST-IN drops below *minloadvoltage*. It continuously transmits the measured values via the serial interface in the format: current[mA] voltage[mV] efficiency[% * 10] (seperated by the SEPERATOR string).

# **Battery Discharge Test**
* Command: "b *maxloadcurrent[mA: 17..5000]* *minloadvoltage[mV: 0..26000]*"
* Example: "l 1000 2700"
* The Power Analyzer sets a constant current load of *maxloadcurrent*. If the voltage drops below *minloadvoltage* it constantly decreases the load to maintain *minloadvoltage*. It stops automatically if the load current drops to 0mA. It continuously transmits the measured values via the serial interface in the format: time[s] current[mA] voltage[mV] capacity[mAh] (seperated by the SEPERATOR string).

# **Long-Term Multimeter**

* Command: "m *interval[ms: 2..65535]* *duration[s: 1..65535]*"
* Example: "m 18000 18000"
* The Power Analyzer measures voltage, current and power delivered to the test device at every *interval* for a total of *duration*. It continuously transmits the measured values via the serial interface in the format: time[ms] current[mA] voltage[mV] (seperated by the SEPERATOR string).

# **Commands for Direct Control**
| Command | Function |
| ------- | -------- |
| "i" | transmits indentification string ("Power Analyzer") |
| "v" | transmits firmware version number |
| "x" | terminate current test program |
| "s *loadcurrent[mA]*" | set load to a constant current of *loadcurrent* |
| "r" | reset the load to minimum |
| "t" | read current and voltage of both sensors and transmit them |
# 4. Notes
* Use a good heatsink with a 5V fan for the MOSFET! Attach a 10K 3950B NTC thermistor to the heatsink close to the MOSFET!
* Be careful with high power loads! Make some tests to figure out what can be achieved with your cooling solution!
* Due to the limitations of the cheap OpAmp the minimum load current is around 17mA. You can choose a better OpAmp if you like (must have same pinout, must be rail-to-rail and unity gain stable), but for most cases this is not necessary.
* The maximum load current is 5A, however for small voltages it might be less.
* The maximum PWR-IN/PWR-OUT current is 8A.
* Do not exceed the maximum voltage of 26V on all connectors !
* In order to make the design much simpler all connectors including USB share a common ground. Keep this in mind when making your test setup in order to avoid ground loops or shorts. Using a USB isolator between the Analyzer and your PC is not a bad idea!
* Windows users may need to install a driver: [http://www.wch.cn/download/CH341SER_ZIP.html](http://www.wch.cn/download/CH341SER_ZIP.html). This is not necessary for linux users.
* You need a UPDI programmer for uploading the firmware.
# 2. Working Principle
The ATtiny814 controls the electronic dummy load with its internal digital to analog converter (DAC). All of its 5 internal reference voltages are being used in order to get the maximum accuracy and resolution of the DAC. The DAC is connected to an OpAmp which acts as a unity gain amplifier controlling the resistance of the MOSFET. Voltage and current are measured via a high side 8 mOhm shunt resistor connected to an INA219 with a resolution of 4mV/1mA. A second INA219 is connected to another 8 mOhm shunt resistor between the PWR-IN and PWR-OUT terminal. The Power Analyzer is connected via USB to a PC or a RaspberryPi. Commands to the Analyzer can be sent via a serial monitor or by the GUI-based Python skript. The Analyzer has different built-in automatic test algorithms. The collected data is sent back via the serial interface/USB to the PC/RaspberryPi. The ATtiny814 constantly measures power and temperature of the heatsink. It controls the fan and cuts off the load when the temperature gets too hot.

# 3. Test Algorithms
* Using a serial monitor: Test algorithms can be started by sending the corresponding command via a serial monitor. The collected data will be displayed in the serial monitor and can be exported to a spread sheet program for further analysis.
* Using the GUI-based python application: This is the easy way. Everything should be self-explanatory. All following example pictures are created by this application.
# **Load Test**

* Command: "l *maxloadcurrent[mA: 17..5000]* *minloadvoltage[mV: 0..26000]*"
* Example: "l 2500 4200"
* The Power Analyzer continuously increases the load from 17 mA up to *maxloadcurrent*. It stops automatically if the voltage drops below *minloadvoltage*. It continuously transmits the measured values via the serial interface in the format: current[mA] voltage[mV] power[mW] (seperated by the SEPERATOR string).

# **Voltage Regulation Test**

* Command: "g *maxloadcurrent[mA: 17..5000]*"
* Example: "g 3000"
* The Power Analyzer changes rapidly the load between 17 mA and *maxloadcurrent*. It continuously transmits the measured values via the serial interface in the format: time[ms] current[mA] voltage[mV] (seperated by the SEPERATOR string).

# **Efficiency Test**

* Command: "e *maxloadcurrent[mA: 17..5000]* *minloadvoltage[mV: 0..26000]*"
* Example: "e 4000 2500"
* The Power Analyzer continuously increases the load from 17 mA up to *maxloadcurrent*. It stops automatically if the voltage at TEST-IN drops below *minloadvoltage*. It continuously transmits the measured values via the serial interface in the format: current[mA] voltage[mV] efficiency[% * 10] (seperated by the SEPERATOR string).

# **Battery Discharge Test**

* Command: "b *maxloadcurrent[mA: 17..5000]* *minloadvoltage[mV: 0..26000]*"
* Example: "l 1000 2700"
* The Power Analyzer sets a constant current load of *maxloadcurrent*. If the voltage drops below *minloadvoltage* it constantly decreases the load to maintain *minloadvoltage*. It stops automatically if the load current drops to 0mA. It continuously transmits the measured values via the serial interface in the format: time[s] current[mA] voltage[mV] capacity[mAh] (seperated by the SEPERATOR string).

# **Long-Term Multimeter**

* Command: "m *interval[ms: 2..65535]* *duration[s: 1..65535]*"
* Example: "m 18000 18000"
* The Power Analyzer measures voltage, current and power delivered to the test device at every *interval* for a total of *duration*. It continuously transmits the measured values via the serial interface in the format: time[ms] current[mA] voltage[mV] (seperated by the SEPERATOR string).

# **Commands for Direct Control**
| Command | Function |
| ------- | -------- |
| "i" | transmits indentification string ("Power Analyzer") |
| "v" | transmits firmware version number |
| "x" | terminate current test program |
| "s *loadcurrent[mA]*" | set load to a constant current of *loadcurrent* |
| "r" | reset the load to minimum |
| "t" | read current and voltage of both sensors and transmit them |
# 4. Notes
* Use a good heatsink with a 5V fan for the MOSFET! Attach a 10K 3950B NTC thermistor to the heatsink close to the MOSFET!
* Be careful with high power loads! Make some tests to figure out what can be achieved with your cooling solution!
* Due to the limitations of the cheap OpAmp the minimum load current is around 17mA. You can choose a better OpAmp if you like (must have same pinout, must be rail-to-rail and unity gain stable), but for most cases this is not necessary.
* The maximum load current is 5A, however for small voltages it might be less.
* The maximum PWR-IN/PWR-OUT current is 8A.
* Do not exceed the maximum voltage of 26V on all connectors !
* In order to make the design much simpler all connectors including USB share a common ground. Keep this in mind when making your test setup in order to avoid ground loops or shorts. Using a USB isolator between the Analyzer and your PC is not a bad idea!
* Windows users may need to install a driver: [http://www.wch.cn/download/CH341SER_ZIP.html](http://www.wch.cn/download/CH341SER_ZIP.html). This is not necessary for linux users.
* You need a UPDI programmer for uploading the firmware.

!注意:请使用浏览器自带下载,迅雷等下载软件可能无法下载到有效资源。
| 器件 | 类型 | 描述 | 数据手册 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LMV321-TR | 低功耗运放 | 点击下载 | |
| 1N4148W | 开关二极管 | 点击下载 | |
| SI2302-HXY | 场效应管(MOSFET) | 点击下载 | |
| JL301-50002U02 | 螺钉式接线端子 | 点击下载 | |
| RCT0310KFLF | 贴片电阻 | 阻值(欧姆):10K 精度:±1% 功率:1/10W 温度系数:- | 点击下载 |
| IRL540NPBF | MOS(场效应管) | 漏源电压(Vdss):100V 连续漏极电流(Id)(25°C 时):36A 栅源极阈值电压:2V @ 250uA 漏源导通电阻:44mΩ @ 18A,10V 最大功率耗散(Ta=25°C):140W 类型:N沟道 N沟道 | 点击下载 |
| ATTINY814-SSNR | MICROCHIP(美国微芯) | 工作电压:1.8V ~ 5.5V CPU位数:8-Bit CPU内核:AVR 主频(MAX):20MHz ROM类型:FLASH ATtiny Series 20MHz 8KB Flash 512B SRAM 8-Bit MCU | 点击下载 |
| X6511WR-02H-C30D60-R2 | 排针 | 点击下载 | |
| INA219AIDR | 电流监控芯片 | 共模输入电压:0V ~ 26V 增益(放大倍数):- 通道数:1 运放类型:Current Sense 监控类型:High Side 工作带宽:- 工作电压:3V ~ 5.5V | 点击下载 |
| 0603B225K100NT | 贴片电容 | 精度:±10% 容值:2.2uF 额定电压:10V 温漂系数(介质材料):X7R 材质:X7R | 点击下载 |
| 25V47uF CD110 | 直插铝电解电容 | 点击下载 | |
| TLMO1100-GS08 | 发光二极管/LED | 点击下载 | |
| WW25WR300FTL | 贴片低阻值采样电阻 | 功率:1W 精度:±1% 阻值(欧姆):0.3 温度系数:±100 ppm/℃ | 点击下载 |
| 73M1R008G | 电流采样电阻/分流器 | 点击下载 | |
| SS54A | 肖特基二极管 | 点击下载 |

欢迎加入EEWorld参考设计群,也许能碰到搞同一个设计的小伙伴,群聊设计经验和难点。 入群方式:微信搜索“helloeeworld”或者扫描二维码,备注:参考设计,即可被拉入群。 另外,如您在下载此设计遇到问题,也可以微信添加“helloeeworld”及时沟通。

EEWorld Datasheet 技术支持